Creating a Node-RED flow with simulated PackML data
4 minute read
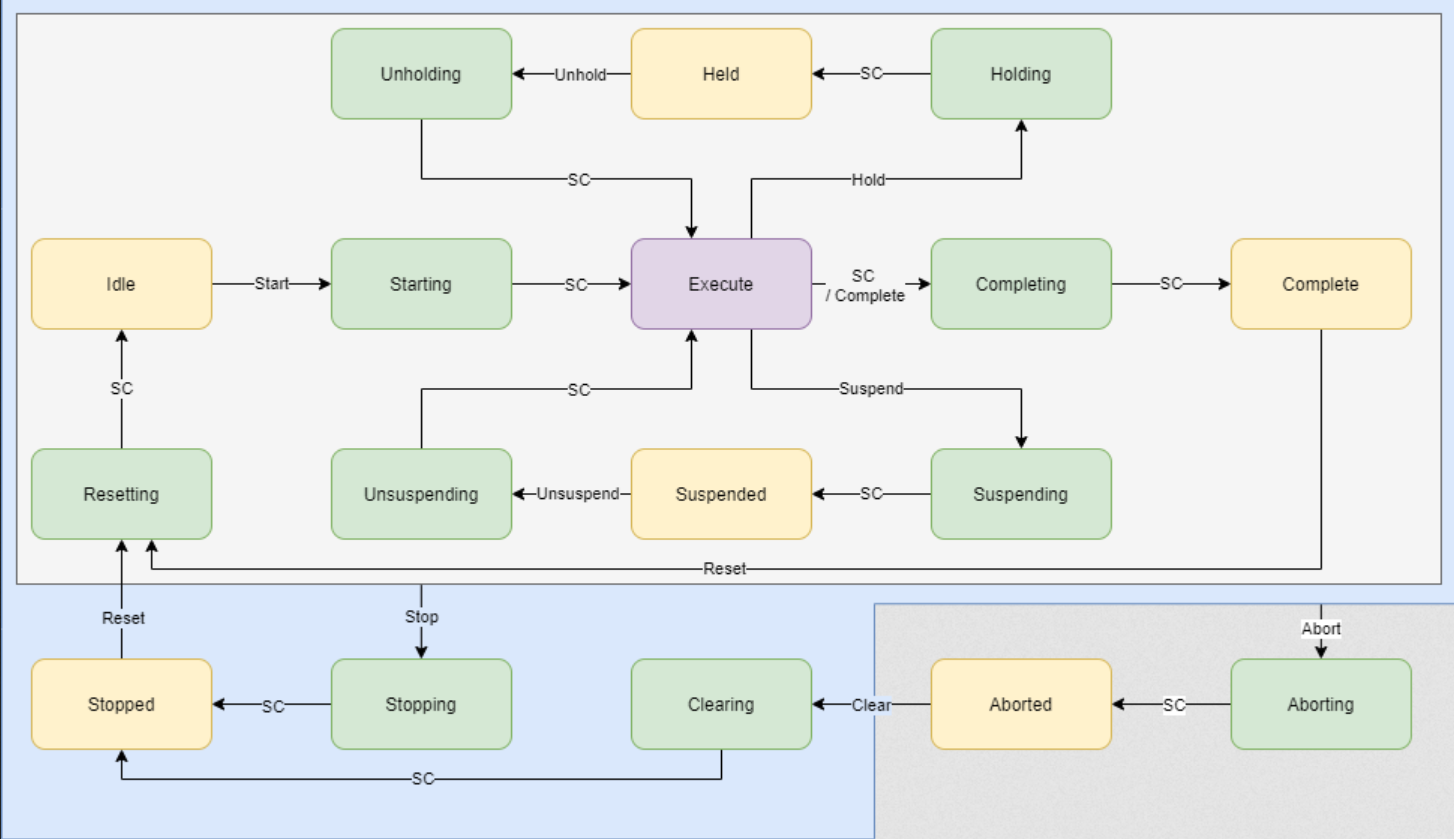
1. Creating a PackML Node-RED-Flow
If you want to download the flow directly, make sure to visit our Node-Red libary.
If you are using a virtual machine type in your browser
localhost:1880/noderedor use the port-forwarding feature from UMHLens.If you are using an edge device type in your browser
(ip of edge-device):1880/nodered.You should now see an empty Node-RED flow if everything is working correctly.
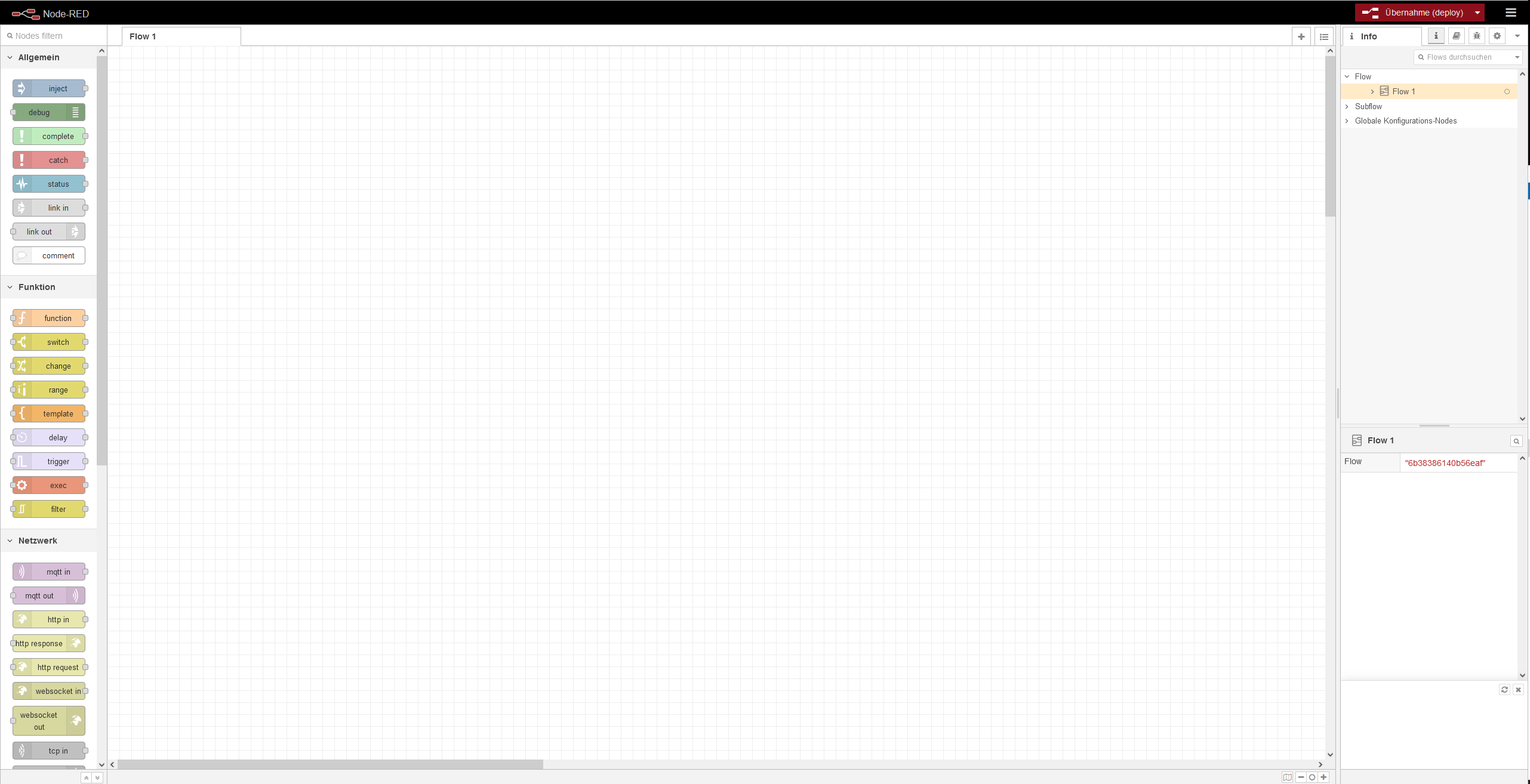
1.1 Converting states into usable data
Our first set of flows will give us the current state of our simulated production line. Therefore, we are converting the packML state structure into the UMH data model. If you want to learn more about the UMH data model visit our documentation. Now drag the following nodes into your flow: mqtt-in→filter→json→switch→function(10x)→mqtt-out.
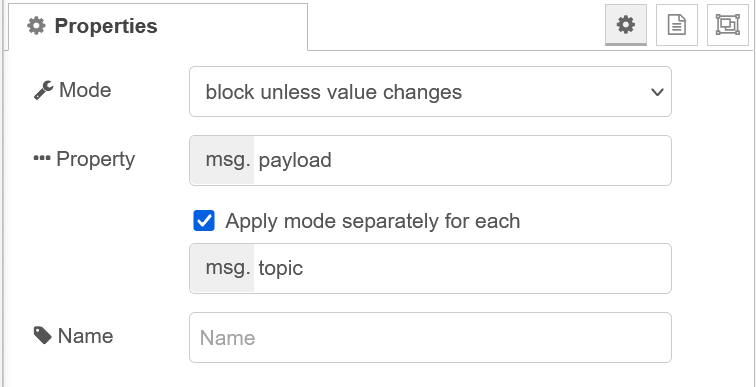
Open the filter-node and set it to block unless value changes
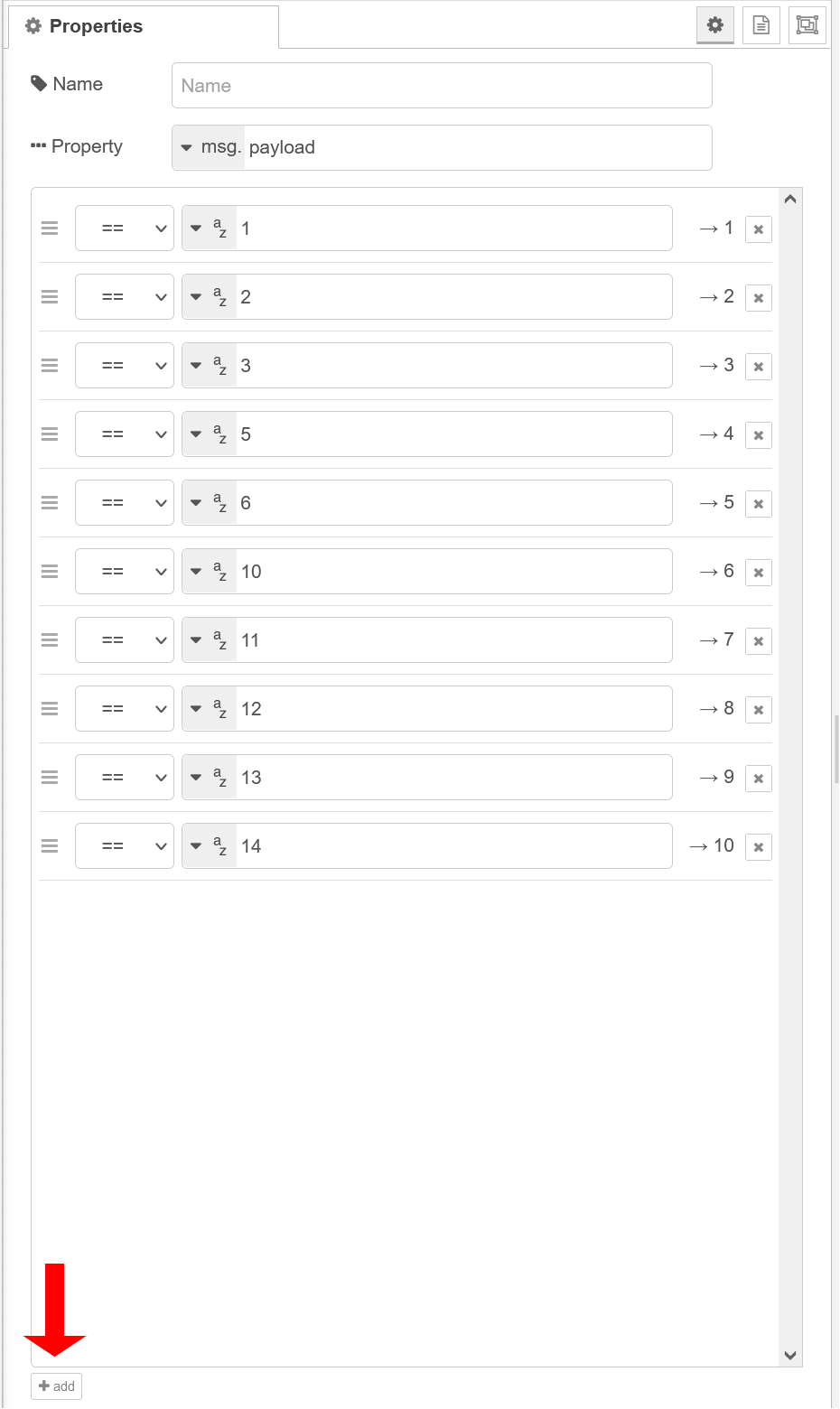
Open the switch-node and configure it as shown below. The switch node will check if the incoming message has one of the values we’ve configured and pass it to the correct function-node.
Now connect all nodes.
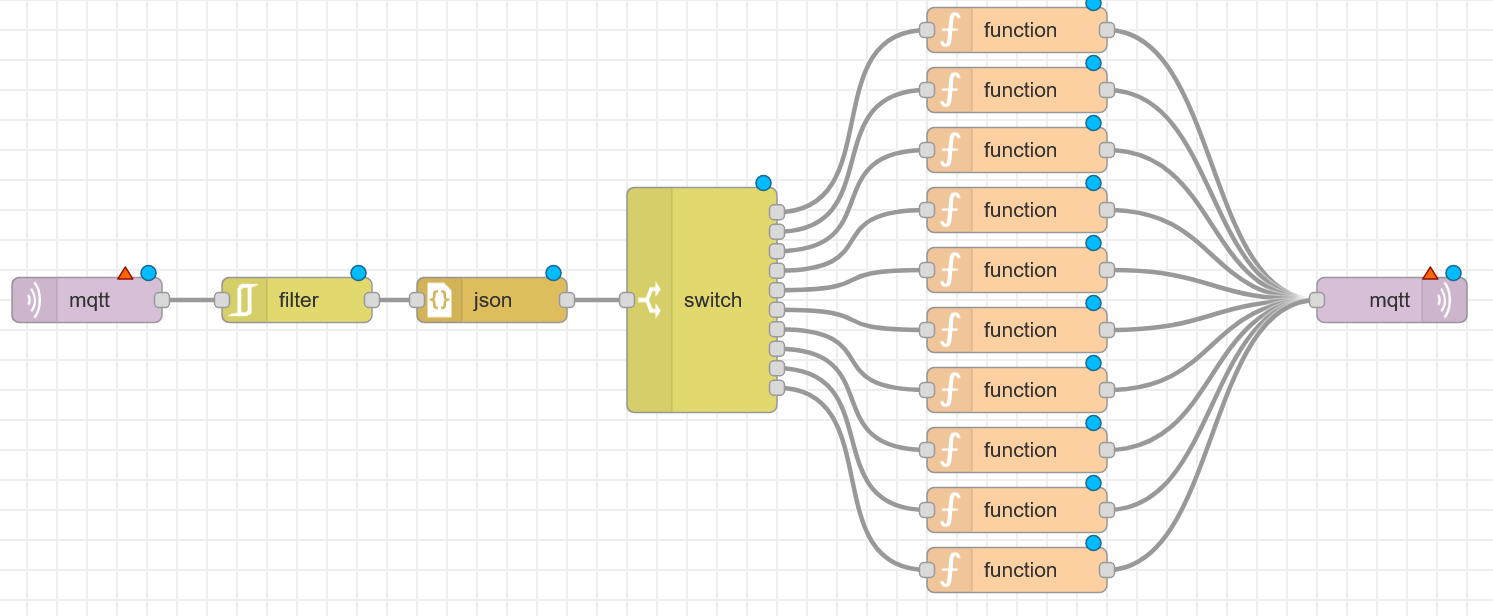
Next up, we need to configure the 10 function-nodes, which will convert the incoming message (Pack-ML state) into the UMH state. If you want to see all UMH states click here. Paste in the following code for each function-node starting from top→bottom.
msg.payload = {"state":40000, "timestamp_ms":Date.now()} return msg;msg.payload = {"state":40000, "timestamp_ms":Date.now()} return msg;msg.payload = {"state":40000, "timestamp_ms":Date.now()} return msg;msg.payload = {"state":90000, "timestamp_ms":Date.now()} return msg;msg.payload = { "state":10000, "timestamp_ms":Date.now()} return msg;msg.payload = {"state":20000, "timestamp_ms":Date.now()} return msg;msg.payload = {"state":220000, "timestamp_ms":Date.now()} return msg;msg.payload = {"state":20000, "timestamp_ms":Date.now()} return msg;msg.payload = {"state":20000, "timestamp_ms":Date.now()} return msg;msg.payload = {"state":20000, "timestamp_ms":Date.now()} return msg;Next, we configure our mqtt-nodes. Paste for the mqtt-in-node in server your edgedive’s IP and in topic
testLocation/DefaultArea/DefaultProductionLine/Status/StateCurrent. And for the mqtt-out-node in server your edgedevice’s IP and in topicia/factoryinsight/Aachen/testAsset/state. Hit deploy on the top right and if everything is working, it should look like something shown below.️ In the latest Version you have to use the service name of hivemq as ip (located in openlens under services→name). You also have to configure the security tab with username:node-redand password:INSECURE_INSECURE_INSECURE)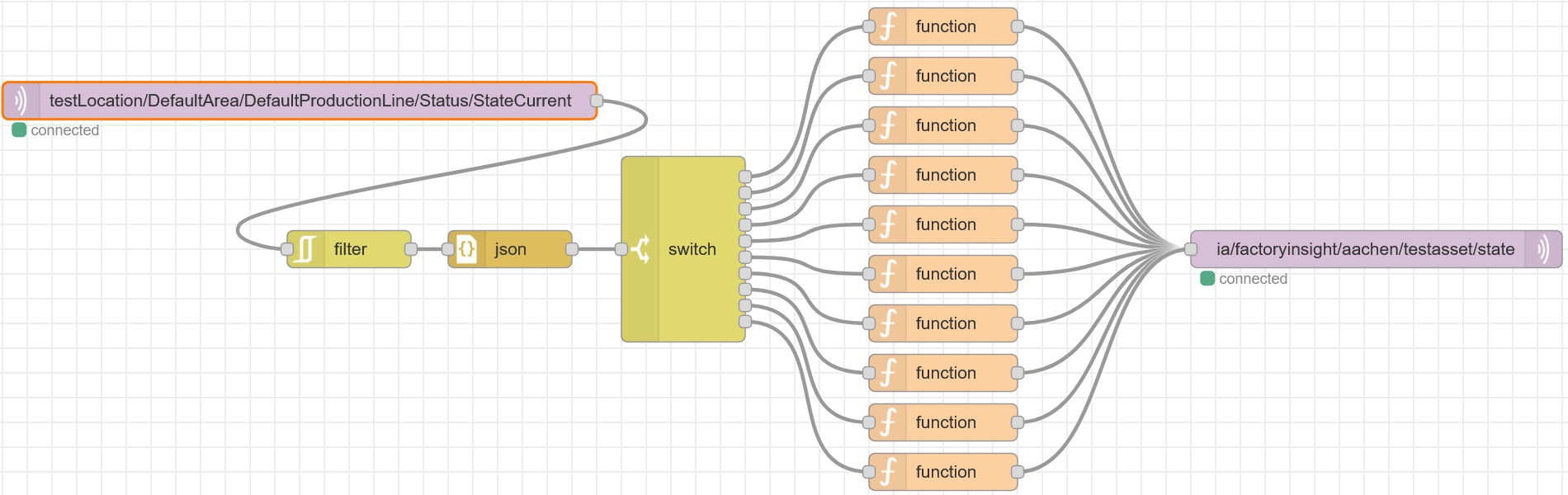
1.2 Machine processing speed
The next set of nodes will return the speed at which the machine is operating. First, drag the following nodes into your flow: mqtt-in→json→function→mqtt-out. Configure the mqtt-in node with the topic ****
testLocation/DefaultArea/DefaultProductionLine/Status/CurMachSpeedand the mqtt-out node with the topicia/factoryinsight/aachen/maschine/processValue.
Next, we need to convert the current machine speed into a percentage number. Therefore, open the function node and paste in the following:
msg.payload = { //creating an object with key:value pairs "timestamp_ms":Date.now(), "CurrentState":parseFloat(msg.payload/102) //maximum speed is 102 } return msg;Click deploy on the top right, and you are done with this set of nodes.
1.3 Good and defective produced products
The last set of nodes will count the good and defective produced products. Since this simulator already gives us the total number of defective and good products, we have to convert that, so that every time a product is produced (defective or good) we get a count signal. Import two mqtt-in, two json, three function, and one mqtt-out node into your flow.
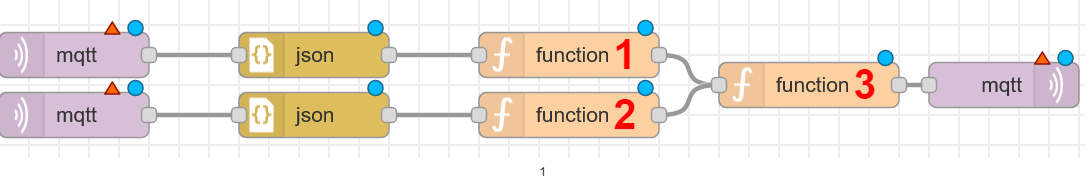
Paste this code into function1 → On Start. The code will be run once on start.
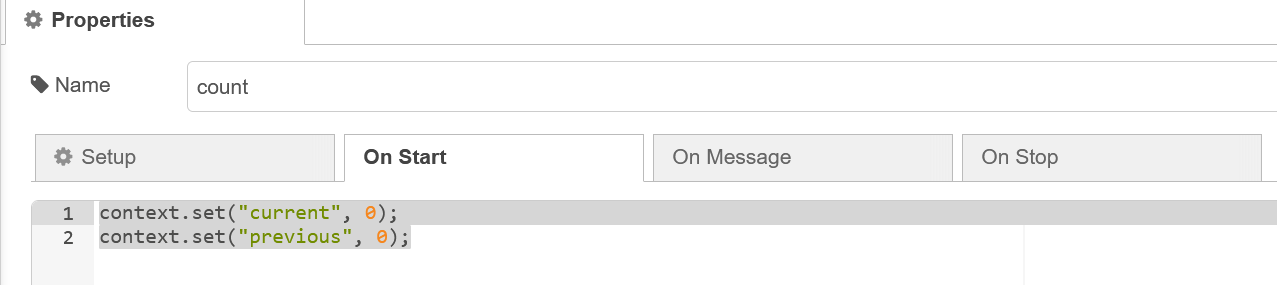
context.set("current", 0); context.set("previous", 0);Paste this code into function1 → On Message. The code will be run when a new message appears.
context.set("previous", context.get("current")) context.set("current", msg.payload) msg.payload = { "count":parseInt(context.get("current")-context.get("previous")) } return msg;Now repeat these two steps for function2. Code for function2 → On Start:
context.set("scrapcurrent", 0); context.set("scrapprevious", 0);Code for function2 → On Message:
context.set("scrapprevious", context.get("scrapcurrent")); context.set("scrapcurrent", msg.payload); msg.payload = { "scrap":parseInt(context.get("scrapcurrent")-context.get("scrapprevious")) } return msg;For function3 you only need to paste code into On Message:
msg.payload = { "timestamp_ms":Date.now(), "count":parseInt(msg.payload.count ? msg.payload.count : 0), "scrap":parseInt(msg.payload.scrap ? msg.payload.scrap : 0), } msg.topic = "ia/factoryinsight/aachen/mach/count"; //mqtt-out topic return msg;Since we already specified our mqtt-out topic in the last function node, we only need to configure our mqtt in nodes, with the upper one having the topic:
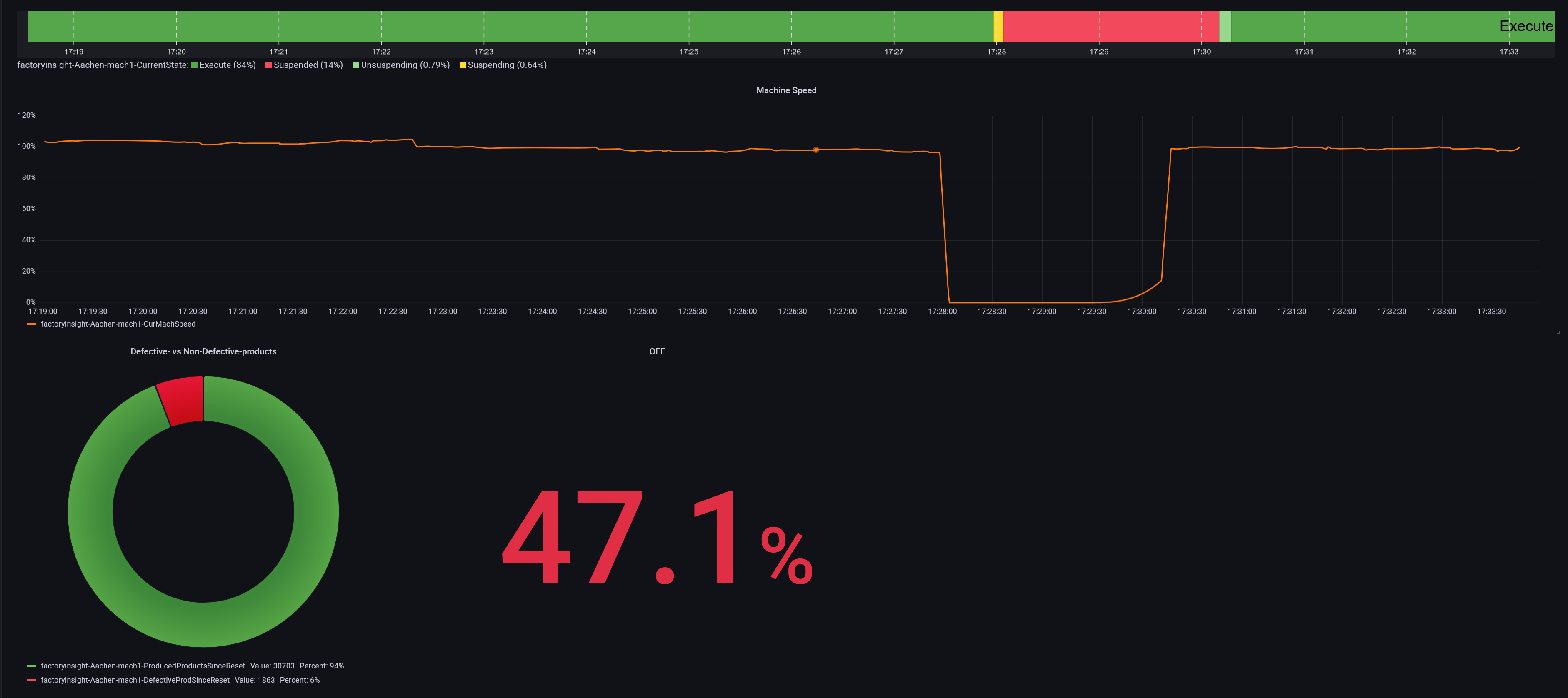
testLocation/DefaultArea/DefaultProductionLine/Admin/ProdProcessedCount/0/Countand the lower one:testLocation/DefaultArea/DefaultProductionLine/Admin/ProdDefectiveCount/0/Count.To make our changes effective, open the mqtt-out node and click done. Finally click deploy.If you want to display your created data, make sure to follow our guide. This flow will look something like this in Grafana:
What’s next?
Make sure to go back to our Getting Started page to follow our Getting-Started-Guide!
Next up is Data Visualization, but you can also try out other data-simulators like the MQTT-Data-Simulator or the OPC-UA-Simulator.