Local minikube installation
4 minute read
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to deploy the UMH stack using minikube, a tool to quickly spin up a Kubernetes cluster in your local machine. This method is quicker than using a virtual machine with k3os, but less reliable. We suggest using minikube only for small tests.
If you are using a different way to install the software, make sure to install the following versions. Specifically installing minikube directly from the website results in a new version, which is not supported yet. Older versions are also not supported anymore.
- minikube 1.26.1
- Kubernetes 1.24.3
- Helm 3.10
Requirements
- Operating system (64-bit):
- Windows 10 version 2004 and higher or Windows 11
- Hardware:
- CPU: 2 cores or more
- RAM: 8GB or more
- Storage: 10GB free
Dependencies
- Verify that you have WSL installed.
- Open Powershell and type
wsl --status. If you get an error you probably need to install it. Refer to the Microsoft documentation on how to do that.
- Open Powershell and type
- Docker Desktop
- You can follow the Docker documentation here.
- Chocolatey
- Read how to do that here.
Installation
Open a PowerShell terminal. Be sure to use the option Run as Administrator.
Install minikube
choco install minikubewhen using Ubuntu you can also use the following command
curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/v1.26.1/minikube-linux-amd64 && sudo install minikube-linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/minikubeInstall helm
choco install kubernetes-helmInstall kubectl
choco install kubernetes-cliSet the default driver for minikube. We recommend Docker, but you can use a variety of drivers. Read the Minikube docs for further information.
minikube config set driver dockerStart an instance of minikube with 2 CPUs and 4GB of RAM. You may need more if you decide to customize the services with the
development.yamlfile.minikube start --cpus 2 --memory 4096Create a namespace in Kubernetes
kubectl create namespace united-manufacturing-hubAdd the UMH repo
helm repo add united-manufacturing-hub https://repo.umh.app/Ensure it is up-to-date with
helm repo updateInstall the stack
helm install united-manufacturing-hub united-manufacturing-hub/united-manufacturing-hub -n united-manufacturing-hubGet the Helm config to import into UMHLens
kubectl config viewOpen UMHLens on your device. You can get UMHLens for free from this GitHub Repository.
Sometimes UMHLens automatically creates a minikube-Cluster. Click on Browse-Clusters to check. If there is no cluster you have to create it manually (follow step 14-18) otherwise continue with step 19.
Click the three horizontal lines in the upper left corner and choose files → preferences
Click on Kubernetes and select “Add custom repo”, type in
https://repo.umh.appas the URL and decide on a name for the repository.Click again file → Add Cluster
Paste the clipboard (which you got from
kubectl config view) into the kubectl prompt of UMHLens.Click on Add Cluster.
Click on Browse Clusters in Catalog, then connect to the Cluster.
Click on Helm -> Releases and change the namespace from default to united-manufacturing-hub in the upper right corner
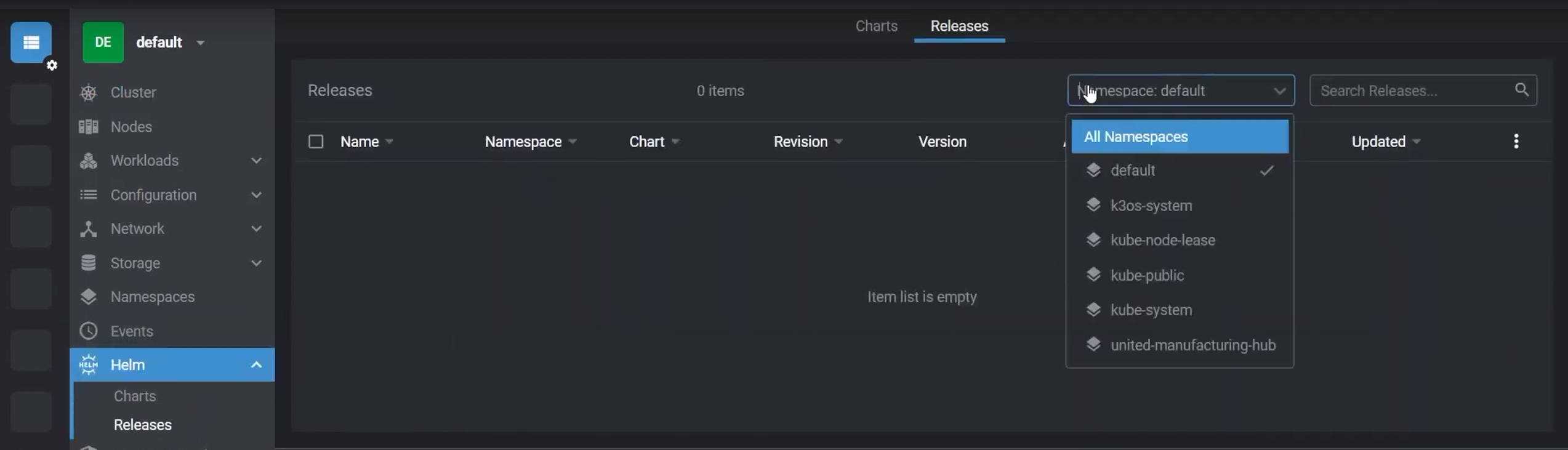
Click on the Release
united-manufacturing-hubto be able to inspect the values.yaml file, which holds the configurations of all microservices used in the cluster.
Enable minikube ingress
minikube addons enable ingressminikube tunnel
Now it should look like this:
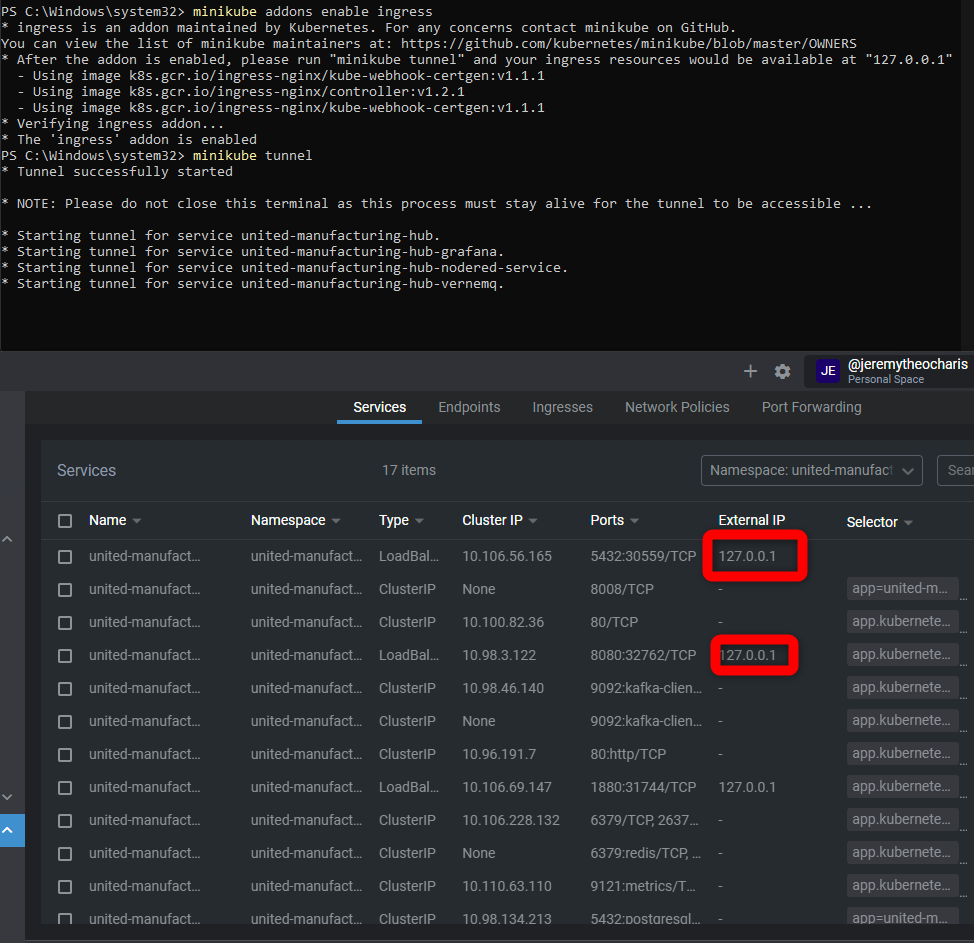
Any you can access Node-RED e.g., via localhost:1880/nodered
This tunnel needs to be always started using minikube tunnel when you want to access these services.
What’s next
You have successfully deployed the UMH stack using minikube.
The next step will be to gather some kind of data, and since you did a local installation you probably want to simulate it. We have a guide to generate data with an MQTT Simulator.
You could also directly connect NodeRED without having data. Follow this guide to see how.
If you are not sure on what to do you can get back to the Getting Started page.
Advanced: run multiple clusters
You can run multiple clusters of minikube by simply using minikube start -p newcluster. This creates a new cluster (called “Profile” in minikube) with the name newcluster.
To switch between the profiles you can use minikube profile <profilename>.
kubectl will automatically change its scope whenever you switch profile.
Learn more about profiles in the minikube documentation.