2.1 Automation pyramid
One of the central frameworks in the world of OT, is the automation pyramid, international standards ISA-95 or IEC62264. This framework will be briefly explained in this section.
2 minute read
OT is the hardware and software to manage, monitor and control industrial operations. Its tasks range from monitoring critical assets to controlling robots on the shop floor. It basically keeps machines and factories running and producing the required product.
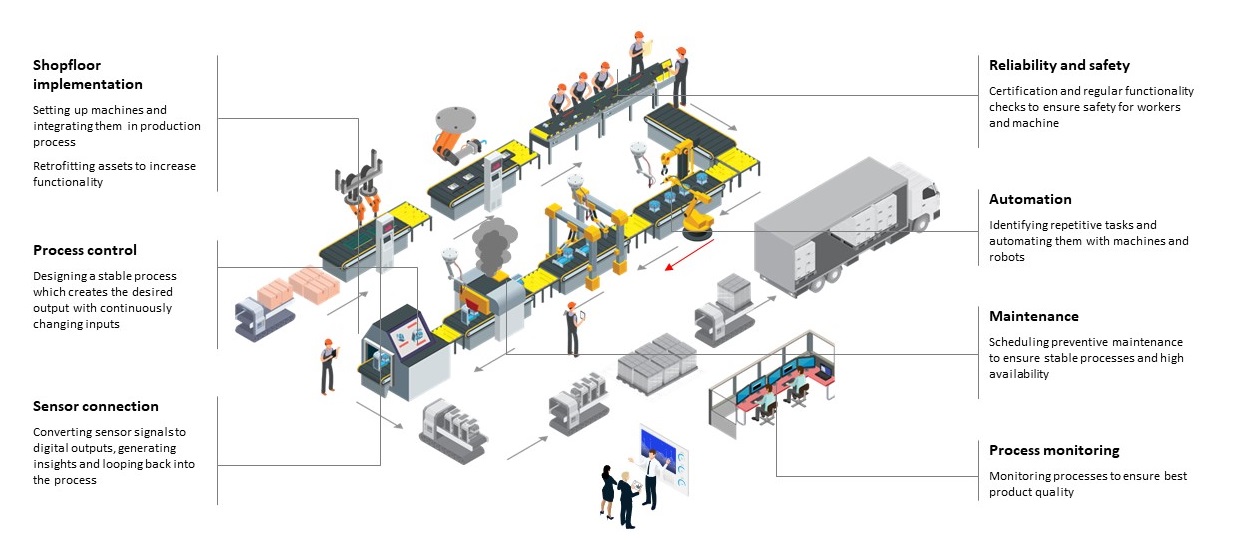
As you can see, OT has a wide array of topics to handle: from process monitoring and control, over safety and implementation concerns, to automation and maintenance.
Nobody wants to build a nuclear reactor using agile “move fast, break things” principles
As promised, this is similar to what we’ve seen earlier in the Information Technology chapter
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Reliability & Safety | Malfunction can result in extreme damages to human and property |
| Maintainability & standards | Machines typically run between 20-30 years, sometimes even 50+ years |
| Certifications | Legally required certifications for safety and optional certificates for reliability |
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| User experience | OT programmer are usually not specifically trained to supply a quality UX |
| Quick development cycles, e.g., agile | Can result in missing out important safety elements and damage workers or machines |
| IT Security | Since machines can run decades unchanged, IT security needs to be addressed outside on a network-level |
Take a look at the following chapters and if you know these topics (as they will become relevant in chapter 3: Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)).
One of the central frameworks in the world of OT, is the automation pyramid, international standards ISA-95 or IEC62264. This framework will be briefly explained in this section.
How to control production machines? Programmable Logic Controller, PID controls and more
As referred in the chapter Automation pyramid, on the layer 3 the software system defined is MES and on layer 4 ERP and PLM. These software systems will be explained in the current section in detail.
Lean Management optimises processes by reducing time spent on non-value-added tasks (unnecessary operations or transport, waiting, overproduction, etc.), causes of poor quality and complications
Retrofitting is the strategy used to enhance capabilities of machine. By adding sensors, the team can generate insights of a machine or a production process in an indirect manner, improving their initial capabilities.
Data Historians are time series databases specifically for OT purposes